 java.awt.FlowLayout
java.awt.FlowLayout
|
Java™ Platform Standard Ed. 6 |
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
java.lang.Objectjava.awt.FlowLayout
public class FlowLayout
A flow layout arranges components in a directional flow, much
like lines of text in a paragraph. The flow direction is
determined by the container's componentOrientation
property and may be one of two values:
ComponentOrientation.LEFT_TO_RIGHT
ComponentOrientation.RIGHT_TO_LEFT
align
property. The possible values are:
For example, the following picture shows an applet using the flow layout manager (its default layout manager) to position three buttons:
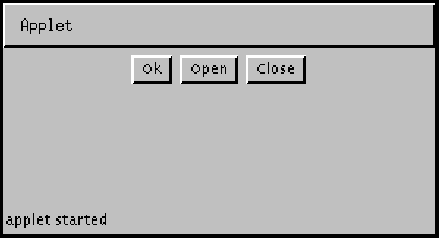
Here is the code for this applet:
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class myButtons extends Applet {
Button button1, button2, button3;
public void init() {
button1 = new Button("Ok");
button2 = new Button("Open");
button3 = new Button("Close");
add(button1);
add(button2);
add(button3);
}
}
A flow layout lets each component assume its natural (preferred) size.
ComponentOrientation,
Serialized Form| Field Summary | |
|---|---|
static int |
CENTER
This value indicates that each row of components should be centered. |
static int |
LEADING
This value indicates that each row of components should be justified to the leading edge of the container's orientation, for example, to the left in left-to-right orientations. |
static int |
LEFT
This value indicates that each row of components should be left-justified. |
static int |
RIGHT
This value indicates that each row of components should be right-justified. |
static int |
TRAILING
This value indicates that each row of components should be justified to the trailing edge of the container's orientation, for example, to the right in left-to-right orientations. |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
FlowLayout()
Constructs a new FlowLayout with a centered alignment and a
default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap. |
|
FlowLayout(int align)
Constructs a new FlowLayout with the specified
alignment and a default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap. |
|
FlowLayout(int align,
int hgap,
int vgap)
Creates a new flow layout manager with the indicated alignment and the indicated horizontal and vertical gaps. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
void |
addLayoutComponent(String name,
Component comp)
Adds the specified component to the layout. |
int |
getAlignment()
Gets the alignment for this layout. |
boolean |
getAlignOnBaseline()
Returns true if components are to be vertically aligned along their baseline. |
int |
getHgap()
Gets the horizontal gap between components and between the components and the borders of the Container |
int |
getVgap()
Gets the vertical gap between components and between the components and the borders of the Container. |
void |
layoutContainer(Container target)
Lays out the container. |
Dimension |
minimumLayoutSize(Container target)
Returns the minimum dimensions needed to layout the visible components contained in the specified target container. |
Dimension |
preferredLayoutSize(Container target)
Returns the preferred dimensions for this layout given the visible components in the specified target container. |
void |
removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)
Removes the specified component from the layout. |
void |
setAlignment(int align)
Sets the alignment for this layout. |
void |
setAlignOnBaseline(boolean alignOnBaseline)
Sets whether or not components should be vertically aligned along their baseline. |
void |
setHgap(int hgap)
Sets the horizontal gap between components and between the components and the borders of the Container. |
void |
setVgap(int vgap)
Sets the vertical gap between components and between the components and the borders of the Container. |
String |
toString()
Returns a string representation of this FlowLayout
object and its values. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
|---|
public static final int LEFT
public static final int CENTER
public static final int RIGHT
public static final int LEADING
Component.getComponentOrientation(),
ComponentOrientation,
Constant Field Valuespublic static final int TRAILING
Component.getComponentOrientation(),
ComponentOrientation,
Constant Field Values| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public FlowLayout()
FlowLayout with a centered alignment and a
default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap.
public FlowLayout(int align)
FlowLayout with the specified
alignment and a default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap.
The value of the alignment argument must be one of
FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.RIGHT,
FlowLayout.CENTER, FlowLayout.LEADING,
or FlowLayout.TRAILING.
align - the alignment value
public FlowLayout(int align,
int hgap,
int vgap)
The value of the alignment argument must be one of
FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.RIGHT,
FlowLayout.CENTER, FlowLayout.LEADING,
or FlowLayout.TRAILING.
align - the alignment valuehgap - the horizontal gap between components
and between the components and the
borders of the Containervgap - the vertical gap between components
and between the components and the
borders of the Container| Method Detail |
|---|
public int getAlignment()
FlowLayout.LEFT,
FlowLayout.RIGHT, FlowLayout.CENTER,
FlowLayout.LEADING,
or FlowLayout.TRAILING.
setAlignment(int)public void setAlignment(int align)
FlowLayout.LEFT
FlowLayout.RIGHT
FlowLayout.CENTER
FlowLayout.LEADING
FlowLayout.TRAILING
align - one of the alignment values shown abovegetAlignment()public int getHgap()
Container
ContainersetHgap(int)public void setHgap(int hgap)
Container.
hgap - the horizontal gap between components
and between the components and the borders
of the ContainergetHgap()public int getVgap()
Container.
ContainersetVgap(int)public void setVgap(int vgap)
Container.
vgap - the vertical gap between components
and between the components and the borders
of the ContainergetVgap()public void setAlignOnBaseline(boolean alignOnBaseline)
alignOnBaseline - whether or not components should be
vertically aligned on their baselinepublic boolean getAlignOnBaseline()
public void addLayoutComponent(String name,
Component comp)
addLayoutComponent in interface LayoutManagername - the name of the componentcomp - the component to be addedpublic void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)
removeLayoutComponent in interface LayoutManagercomp - the component to removeContainer.removeAll()public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container target)
preferredLayoutSize in interface LayoutManagertarget - the container that needs to be laid out
Container,
minimumLayoutSize(java.awt.Container),
Container.getPreferredSize()public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container target)
minimumLayoutSize in interface LayoutManagertarget - the container that needs to be laid out
preferredLayoutSize(java.awt.Container),
Container,
Container.doLayout()public void layoutContainer(Container target)
FlowLayout object.
layoutContainer in interface LayoutManagertarget - the specified component being laid outContainer,
Container.doLayout()public String toString()
FlowLayout
object and its values.
toString in class Object
|
Java™ Platform Standard Ed. 6 |
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
Copyright © 1993, 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Use is subject to license terms. Also see the documentation redistribution policy.