- java.lang.Object
-
- javax.swing.SizeSequence
-
public class SizeSequence extends Object
ASizeSequenceobject efficiently maintains an ordered list of sizes and corresponding positions. One situation for whichSizeSequencemight be appropriate is in a component that displays multiple rows of unequal size. In this case, a singleSizeSequenceobject could be used to track the heights and Y positions of all rows.Another example would be a multi-column component, such as a
JTable, in which the column sizes are not all equal. TheJTablemight use a singleSizeSequenceobject to store the widths and X positions of all the columns. TheJTablecould then use theSizeSequenceobject to find the column corresponding to a certain position. TheJTablecould update theSizeSequenceobject whenever one or more column sizes changed.The following figure shows the relationship between size and position data for a multi-column component.
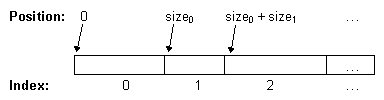
In the figure, the first index (0) corresponds to the first column, the second index (1) to the second column, and so on. The first column's position starts at 0, and the column occupies size0 pixels, where size0 is the value returned by
getSize(0). Thus, the first column ends at size0 - 1. The second column then begins at the position size0 and occupies size1 (getSize(1)) pixels.Note that a
SizeSequenceobject simply represents intervals along an axis. In our examples, the intervals represent height or width in pixels. However, any other unit of measure (for example, time in days) could be just as valid.Implementation Notes
Normally when storing the size and position of entries, one would choose between storing the sizes or storing their positions instead. The two common operations that are needed during rendering are:getIndex(position)andsetSize(index, size). Whichever choice of internal format is made one of these operations is costly when the number of entries becomes large. If sizes are stored, finding the index of the entry that encloses a particular position is linear in the number of entries. If positions are stored instead, setting the size of an entry at a particular index requires updating the positions of the affected entries, which is also a linear calculation.Like the above techniques this class holds an array of N integers internally but uses a hybrid encoding, which is halfway between the size-based and positional-based approaches. The result is a data structure that takes the same space to store the information but can perform most operations in Log(N) time instead of O(N), where N is the number of entries in the list.
Two operations that remain O(N) in the number of entries are the
insertEntriesandremoveEntriesmethods, both of which are implemented by converting the internal array to a set of integer sizes, copying it into the new array, and then reforming the hybrid representation in place.- Since:
- 1.3
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor Description SizeSequence()Creates a newSizeSequenceobject that contains no entries.SizeSequence(int numEntries)Creates a newSizeSequenceobject that contains the specified number of entries, all initialized to have size 0.SizeSequence(int[] sizes)Creates a newSizeSequenceobject that contains the specified sizes.SizeSequence(int numEntries, int value)Creates a newSizeSequenceobject that contains the specified number of entries, all initialized to have sizevalue.
-
Method Summary
Modifier and Type Method Description intgetIndex(int position)Returns the index of the entry that corresponds to the specified position.intgetPosition(int index)Returns the start position for the specified entry.intgetSize(int index)Returns the size of the specified entry.int[]getSizes()Returns the size of all entries.voidinsertEntries(int start, int length, int value)Adds a contiguous group of entries to thisSizeSequence.voidremoveEntries(int start, int length)Removes a contiguous group of entries from thisSizeSequence.voidsetSize(int index, int size)Sets the size of the specified entry.voidsetSizes(int[] sizes)Resets thisSizeSequenceobject, using the data in thesizesargument.
-
-
-
Constructor Detail
-
SizeSequence
public SizeSequence()
Creates a newSizeSequenceobject that contains no entries. To add entries, you can useinsertEntriesorsetSizes.- See Also:
insertEntries(int, int, int),setSizes(int[])
-
SizeSequence
public SizeSequence(int numEntries)
Creates a newSizeSequenceobject that contains the specified number of entries, all initialized to have size 0.- Parameters:
numEntries- the number of sizes to track- Throws:
NegativeArraySizeException- ifnumEntries < 0
-
SizeSequence
public SizeSequence(int numEntries, int value)Creates a newSizeSequenceobject that contains the specified number of entries, all initialized to have sizevalue.- Parameters:
numEntries- the number of sizes to trackvalue- the initial value of each size
-
SizeSequence
public SizeSequence(int[] sizes)
Creates a newSizeSequenceobject that contains the specified sizes.- Parameters:
sizes- the array of sizes to be contained in theSizeSequence
-
-
Method Detail
-
setSizes
public void setSizes(int[] sizes)
Resets thisSizeSequenceobject, using the data in thesizesargument. This method reinitializes this object so that it contains as many entries as thesizesarray. Each entry's size is initialized to the value of the corresponding item insizes.- Parameters:
sizes- the array of sizes to be contained in thisSizeSequence
-
getSizes
public int[] getSizes()
Returns the size of all entries.- Returns:
- a new array containing the sizes in this object
-
getPosition
public int getPosition(int index)
Returns the start position for the specified entry. For example,getPosition(0)returns 0,getPosition(1)is equal togetSize(0),getPosition(2)is equal togetSize(0)+getSize(1), and so on.Note that if
indexis greater thanlengththe value returned may be meaningless.- Parameters:
index- the index of the entry whose position is desired- Returns:
- the starting position of the specified entry
-
getIndex
public int getIndex(int position)
Returns the index of the entry that corresponds to the specified position. For example,getIndex(0)is 0, since the first entry always starts at position 0.- Parameters:
position- the position of the entry- Returns:
- the index of the entry that occupies the specified position
-
getSize
public int getSize(int index)
Returns the size of the specified entry. Ifindexis out of the range(0 <= index < getSizes().length)the behavior is unspecified.- Parameters:
index- the index corresponding to the entry- Returns:
- the size of the entry
-
setSize
public void setSize(int index, int size)Sets the size of the specified entry. Note that if the value ofindexdoes not fall in the range:(0 <= index < getSizes().length)the behavior is unspecified.- Parameters:
index- the index corresponding to the entrysize- the size of the entry
-
insertEntries
public void insertEntries(int start, int length, int value)Adds a contiguous group of entries to thisSizeSequence. Note that the values ofstartandlengthmust satisfy the following conditions:(0 <= start < getSizes().length) AND (length >= 0). If these conditions are not met, the behavior is unspecified and an exception may be thrown.- Parameters:
start- the index to be assigned to the first entry in the grouplength- the number of entries in the groupvalue- the size to be assigned to each new entry- Throws:
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException- if the parameters are outside of the range: (0 <= start < (getSizes().length)) AND (length >= 0)
-
removeEntries
public void removeEntries(int start, int length)Removes a contiguous group of entries from thisSizeSequence. Note that the values ofstartandlengthmust satisfy the following conditions:(0 <= start < getSizes().length) AND (length >= 0). If these conditions are not met, the behavior is unspecified and an exception may be thrown.- Parameters:
start- the index of the first entry to be removedlength- the number of entries to be removed
-
-